What are billfish?
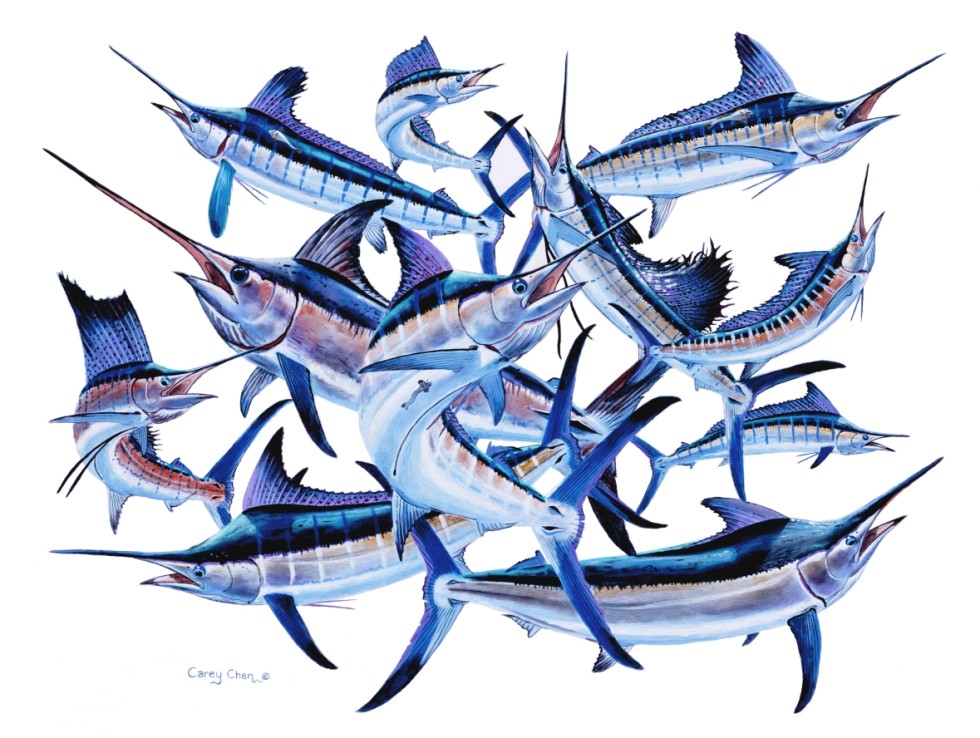

In General Terms- The term “Billfish” refers to various predatory fish species typically belonging to the taxonomical family Istiophoridae. Their biological characteristics include a spear-like rostrum or “bill,” which is used for slashing at and stunning prey. The dorsal fin of these species runs along a large part of their body and narrow pelvic fins. Billfish can be found spread throughout the worlds oceans and are defined as highly migratory species but typically reside in tropical or sub-tropical waters. The prey of these apex predators differs from a variety of small fishes to crustaceans and cephalopods (i.e. squid). Further examination of the various billfish reveals the plethora of biological differences between species.

Black Marlin (Istiompax indica) - The black marlin, primarily found in the Indian and Pacific oceans are primarily distinguished from other billfish by their rigid and broad pectoral fins as well as its comparatively diminished dorsal fin. The coloration of the black marlin is similar to other billfish with a dark blue dorsal side, which fades to silvery-white on the ventral side with faint blue stripes. “Males may reach a length of 4.65 m and weight of 750 kgs, but females are generally much larger.” (Marinebio.org) Black Marlin preferably feed on small tuna but also prey on dolphin, cuttlefish, squid, mackerel, and large crustaceans. Sometimes referred to as the “bull” of the Sea, the black marlin shows incredible strength and do not tire readily when caught. Blacks can be found in near-shore waters and around reefs but are found in scattered numbers in the open sea. Larger black marlin have been caught by anglers off the coast of Australia, Peru, Panama, and Mozambique.
Common Names of Black Marlin (provided by ICCAT):
Denmark: Sort marlin
Ecuador: Merlín negro, Picudo, Picudo negro
Fiji: Saku vorowaqa
Finland: Mustamarliini
India: Tonki, Tadamasa
Italy: Marlin nero, Pesce lancia
Japan: Kurokawa, Shirokajiki
Malaysia: Ikan layer, Layaran, Mersuji, Mersuji hitam, Puoh hu, Suji, Tumbuk banir
Martinique: Varé
Mexico: Marlin negro
Micronesia: Taguraar
Netherlands: Zwarte marlijn
New Zealand: Taketonga
Nicaragua: Aguja negra
Norway: Svart marlin
Oman: Kheil al bahar
Papa New Guinea: Bwagilium
Philippines: Tandalayang, Malasugi, Dol-lakak, Malakay, Malasugue
Portugal: Espadim, Espadim negro, Espadim petro
Russian Fed: Sere bristyi marlin
Samoa: Sa’ula-oso
Somalia: Daanbeeri
South Africa: Swart marlin
Sri Lanka: Ahin kopparsa, Dhappara, Ghappara, Kalu koppara, Makara, Saparava
United States of America: Black marlin

Blue Marlin (Makaira nigricans & Makaira mazara) – Blue Marlin are found throughout the worlds oceans in tropical, subtropical, and temperate waters. The blue marlin is notably the largest of billfish species. Blue marlin are characterized by a cylindrical body shape, two dorsal fins (one with a steep slope and one smaller toward the posterior of the organism), and unlike the black marlin the pectoral fins are not rigid. They are named for their cobalt blue dorsal coloration, which fades into a silvery white. The keels on the caudal peduncle on the blue marlin make it an exceptionally strong and fast swimmer, a trait attractive to many anglers.
There are actually two subspecies of blue marlin, Makaira nigricans & Makaira mazara. Makaira nigricans resides in the Atlantic while Makaira mazara resides in the Indian and Pacific oceans. Those in the Pacific and Indian oceans tend to be larger than those in the Atlantic. While the blue marlin is one of the most sought after species by recreational anglers it is not as abundant as other billfish. Primarily near-surface pelagic fishes such as mackerels, tunas, and dolphin are preyed upon by the blue marlin.
Blue marlin are distinguished from black marlin (Makaira indica) by the non-rigid pectoral fin and the presence of blue bars displayed along the body. The lower dorsal fin height of blue marlin distinguishes it from striped marlin (Tetrapturus audax), whose dorsal fin height is equal to its body depth.
Common Names of Blue Marlin (provided by ICCAT):
Azores Islands: Espadim azul
Barbados: Marlin
Benin: Ajètè, Adjètè
Brazil: Agulhão preto, Agulhão, Marlim-azul
Canada: Makaire bleu
Cape Verde: Espadim-azul, Espadarte, Blue marlin
Côte d’Ivoire: Espadon
Cuba: Aguja casta, Abanico, Voladora
Denmark: Atlantisk blå marlin
Dominican Republic: Aguja azul, Marlin azul
Finland: Sinimarliini
France: Makaire bleu
Germany: Blauer Marlin
Italy: Marlin azzurro, Marlin blu
Japan: Nishikurokajiki
Korea: Nog-sae-chi
Martinique: Makaire bleu, Varé
Mexico: Marlín azul
Morocco: Espadon
Namibia: Blou marlyn
Netherlands Antilles: Balau blanku
Norway: Blå marlin
Portugal: Espadim-azul, Espadarte-sombra
Puerto Rico: Blue marlin
Romania: Marlin albastru
South Africa: Blou marlin
Spain: Marlin azul
Trinidad y Tobago: Maman-balatre, Blue marlin
Uruguay: Marlin azul
United Kingdom: Atlantic blue marlin
United States of America: Atlantic blue marlin
Venezuela: Aguja azul, Marlin azul
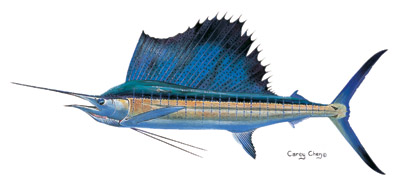
Sailfish (Istiophorus platypterus and Istiophorus albicans)– Sailfish are one of the most iconic billfish easily recognizable by their extremely large and colorful dorsal fins. Found throughout the world, sailfish are divided into two subspecies, Istiophorus platypterus and Istiophorus albicans. Istiophorus platypterus is located in the Pacific and Indian oceans while Istiophorus albicans reside in the Atlantic in both tropical and temperate waters. Like with the blue marlin, sailfish of the Indian and Pacific oceans are much larger than those in the Atlantic. One of the unique characteristics of sailfish is that their coloration is capable of changing with their level of excitement. Typically, the sailfish “body is dark blue dorsally and white with brown spots ventrally. About 20 bars, each consisting of many light blue dots, are present on each side. The fins are all generally blackish blue.” (Florida Museum of Natural History) The sailfish’s primary diet consists of various cephalopods and bony fishes such as needlefish, mackerels, tunas, and jacks.
Common Names of Sailfish (provided by ICCAT):
Azores Islands: Atlantic sailfish
Barbados: Sailfish
Benin: Ajètè-abadanon
Brazil: Agulhão-bandeira, Agulhão de vela
Canada: Sailfish
Cape Verde: Peixe-vela, Veleiro
China:
Côte d’Ivoire: Voilier
Cuba: Aguja voladora, Aguja de abanico, Voladeira
Denmark: Atlantisk sejlfisk
Dominican Republic: Aguja
Finland: Atlantinpurjekala
France: Voilier de l’Atlantique
Germany: Segelfisch
Greece:
Italy: Pesce vela
Japan: Nishibashookajiki
Korea: Dot-sae-chi
Martinique: Voilier de l’Atlantique, Mere balaou
Mexico: Pez vela, Volador
Morocco: Espadon
Netherlands Antilles: Balau wairu, Balau di bandera
Norway: Atlantisk seilfisk
Portugal: Espardarte veleiro, Peixe de vela
Puerto Rico: Sailfish
Russian Fed: Atlanticheskii parusnik, Parusnik-ryba
Senegal: Espadon voilier
South Africa: Seilvis, Sailfish
Spain: Pez vela del Atlántico
Trinidad y Tobago: Sailfish
Uruguay: Pez vela
United Kingdom: Atlantic sailfish
United States of America: Atlantic sailfish
Venezuela: Pez vela, Palagar

Spearfish (Tetrapturus pfluegeri, T. angustirostris, and T. belone) – The spearfish is found throughout the world’s oceans in tropical and subtropical waters. The spearfish has a dorsal fin similar to that of the sailfish but lacks the sailfish’s dorsal height and length. Spearfish feed near the surface on small fish including dolphin, flying fish, and needlefish. Squid is also included in spearfish’s diet. Three species of spearfish have been found: the longbill spearfish (Tetrapturus pfluegeri) located in the northwest Atlantic from New Jersey to Venezuela, including the Gulf of Mexico(this is the most commonly referenced one) the shortbill spearfish (T. angustirostris) located in the Pacific and Indian Oceans; and the Mediterranean spearfish (T. belone) located in the Mediterranean Sea.
Common Names for Longbill Spearfish (provided by ICCAT):
Azores Islands: Longbill spearfish
Benin: Ajètè, Adjètè
Brazil: Agulhão estilete, Marlin-bicudo
Cape Verde: Espadim-bicudo, Marlin-bicudo
Cuba: Aguja
Chinese Taipei: 长吻旗鱼(Chang wen chi yu)
Denmark: Langnæbbet spydfisk
France: Makaire bécune
Germany: Speerfisch, Langschnabliger
Japan: Kuchinagafurai
Martinique: Makaire à longue pectorale, Varé
Mexico: Marlin trompa larga
Netherland Antilles: Balau blanku
Namibia: Langschnauziger Speerfisch, Langbek-speervis
Norway: Spydfisk
Portugal: Espadim bicudo, Marlin bicudo, Espadin aguia
Russian Fed: Malyi kopénosets
South Africa: Langbek-speervis, Longbill spearfish
Spain: Aguja picuda, Romerillo, Saltón
Sweden: Långnosad spjutfisk
United Kingdom: Longbill spearfish
United States of America: Longbill spearfish
Uraguay: Marlín picudo
Venezuela: Aguja corta, Aguja-palagar, Pez lanza, Voladora
Common Names for the Mediterranean Spearfish (provided by ICCAT):
Algeria: Auggia imbriale
Croatia: Jaglun
Denmark: Middelhavsspydfisk
Finland: Marliini
France: Marlin de Méditerranée, Poisson-pique
Greece: , Marlinos mesogiou
Italy: Aguglia imperiale, Aguglia pelerana, Ugulia imperiali
Japan: Chichukaifuurai
Malta: Imsella imperjali, Pastardella, Pixxispad
Monaco: Aguglia impériale
Norway: Middelhav-marlin
Poland: Marlin sródziemnomorski
Portugal: Espadim-do-Mediterrâneo
Serbia-Montenegro: Barikuda
Spain: Marlín del Mediterráneo
Sweden: Medelhavsspjutfisk
Turkey: Marlin baligi, Yelken baligi
United Kingdom: Mediterranean spearfish
United States of America: Mediterranean shortbill spearfish
Common Names for Shortbill Spearfish (provided by ICCAT):
China: 小旗鱼
Denmark: Kortnæbbet spydfisk
Ecuador: Marlín
Finland: Marliini
France: Makaire à rostre court
Germany: Speerfisch
Hawaii: A’u
Italy: Aguglia imperiale
Japan: Fûraikajiki
Mexico: Marlin trompa corta
Mozambique: Espadim de focinto curto
Oman: Kheil
Papua N Guin: Bwagilum
Portugal: Espadim de bico curto
Russian Fed: Kop’jenosjets
Samoa: Sa’ula
Serbia: Iglokljun
Somalia: Daanbeeri cadde
South Africa: Kortbek-speervis
Spain: Marlin trompa corta
Sweden: Kortnosad spjutfisk
Tanzania: Salisuli
United States of America: Shortbill Spearfish

Striped Marlin (Kajikia audax)- Found in the Pacific and Indian oceans the striped marlin typically occupies cooler water than either black or blue marlin. The coloration of this highly migratory species is a dark blue or black dorsal surface fading to a silvery white and is transected laterally with cobalt stripes. The anterior dorsal fin is higher than the greatest depth and then recedes towards the posterior of the fish. The bill of the striped marlin is of medium size and the pectoral fins are more flexible than other species of billfish.
Common Names of Striped Marlin (provided by ICCAT):
Chile: Pez aguja
Denmark: Spydfisk, Stribet marlin
Ecuador: Marlín, Marlin rayado, Picudo gacho
Fiji: Saku vorowaqa
Finland: Juovamarliini
Germany: Gestreifter marlin
Italy: Pesce lancia striato
Japan: Makajiki
Malaysia: Mersuji, Mersuji tahil
Mexico: Agujó, Marlin rayado
Micronesia: Taguraar
Netherlands: Gestreepte marlijn
New Caledonia: Empereur, Marlin rayé
New Zealand: Takeketonga
Nicaragua: Marlin rayado
Norway: Stripet marlin
Oman: Kheil al bahar
Papa N Guin: Bwagilum
Peru: Merlín rayado
Philippines: Dugso, Liplipan, Malasugi
Poland: Marlin pasiasty
Portugal: Espadim raiado
Russian Fed: Polosatii marlin
Samoa: Sa’ula
Somalia: Daanbeeri cadde
South Africa: Gestreepte marlin
Sri Lanka: Habara, Haura, Iri koppara, Seraman koppara
Sweden: Randig marlin, Strimmig spjutfisk
Tanzania: Salisuli, Samsuli
United States of America: Striped marlin

Swordfish (Xiphias gladius)– The swordfish is one of the most adaptive of the various billfish species. It can be found throughout the world’s oceans and has the capability of standing the widest range of temperatures. Swordfish prefer warm water habitats but can also be found where the water temperature is right above freezing. While most other billfish fall under the taxonomical family “Istiophoridae,” the swordfish falls under the family “Xiphiidae.” The bill of the swordfish is longer compared proportionally to the size of its body than other billfish. Its dorsal fins and pectoral fins are rigid and broad while pelvic fins are entirely absent. The coloration is blackish brown on the dorsal side and only fades slightly to a lighter shade below. The swordfish typically preys upon cephalopods and pelagic fishes and the “sword” is used in the acquisition of food due to “slashes” found on remnants of stomach contents.
Common Names of Swordfish (provided by ICCAT):
Albania: Peshku shtize
Algeria: Pez espada
Angola: Agulha, Agulhão, Espadarte, Peixe-agulha
Argentina: Pez espada
Australia: Broadbill, Broadbill swordfish, Swordfish
Azores: Swordfish, Agulhão, Espadarte
Belgium: Swordfish
Brazil: Aguilhão, Espadarte, Espadarte-meca, Meka, Peixe espada
Can Br Colum: Swordfish
Canada: Broadbill swordfish, Swordfish, Espadon
Cape Verde: Espadarte, Furão, Peixe ferro , Peixe-ferro, Espadon, Espadão, Espadarte, Espadim-azul, Peixe- agulha
Chile: Albacora, Pez espada
China: Chien-chi-yu , Ki-hi-khu , Tinmankhu
Cuba: Emperador, Pez espada
Denmark: Sværdfisk
Djibouti: Sword fish, Espadon
Ecuador: Pez espada
Estonia: Swordfish
Faeroe Islands: Svørðfiskur
Finland: Miekkakala
Former USSR: Mech-ryba, Mechenos, Meshvenosouiye
France: Espadon
Germany: Schwertfisch
Greece: Xifias, Xiphías
Japan: Meka, Mekajiki
Hawaii: Broad-bill sword-fish, A’u ku
Iceland: Sverðfiskur
India: Sword fish, Kunga, Tadmachhi, Mas-hibaru, Kuthirameen, Tadmasa
Indonesia: Toda Todak
Ireland: Swordfish, An colgán
Italy: Pei spa, Pesce spada, Pesce spate, Pesse spada, Pisci spada, Pisci spata, Pisci spatu, Puddicinedda, Spadon, Spadottu, Spateddu
Kiribati: Te rakuika, Te sakula
Rep Korea: Whang-sae-chi
Lebanon: Sankeh
Libya: Abucef
Madeira: Peixe-agulha
Malta: Pixxispad, Spada
Marshall Islands: Lokjan
Martinique : Varé, Espadon
Mauritania: Sword fish Espadon Poisson porte-épée
Mauritius: Swordfish Espadon
Mexico: Pez espada
Mozambique: Espadarte
Namibia: Swaardvis, Schwertfisch
Netherlands: Zwaardvis
New Zealand: Broadbill, Broadbill swordfish, Swordfish, Paea
Nicaragua: Pez espada
Niue: Swordfish, Haku
Norway: Sverdfisk
Oman: Kheil al bahar
Papua N Guin: Broadbill swordfish, Swordfish
Peru: Pez espada
Philippines: Big-ho, Big-ho’, Bigo, Bigok, Dugso, Malasugi Malasugi, Malasugi, Dugho, Swordfish, Sibingan, Malasugi, Malasugue, Manumbuk, Palmbela, Dogso, Lumod, Malasugi, Mayas-pas
Poland: Wlócznik
Portugal: Agulha, Agulhao, Catana, Espada, Espadarte, Peixe agulha, Peixe espada, Peixe-agulha
Romania: Peste cu spada, Peste-spada
Seychelles: Swordfish, Espadron
Slovenia: Meèarica
Somalia: Daanbeeri
South Africa: Swaardvis, Broadbill, Swordfish,
Spain: Emperador, Aja para, Chichi spada, Espada, Espardarte, Pez espada
Sri Lanka: Kadu kpooara
St Helena: Swordfish
Sweden: Svärdfisk
Tahiti: Ha’ura
Tanzania: Nduwalo, Sansuli
Togo: Hatalikofi, Espadon
Tuamoto Islands: Hakura
Tunisia: Bou sif.
Turkey: Kiliç baligi
Ukraine: Mech–ryba
United Kingdom (UK): Broadbill, Swordfish
United States of America: Broadbill, Broadbill swordfish, Swordfish
Venezuela: Pez espada
Vietnam: Broadbill swordfish, Cá Mi kim, Ho cá mui kiem
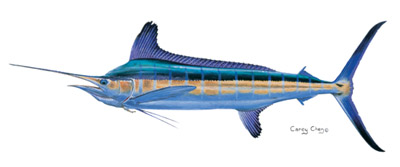
White Marlin (Tetrapturus albidus) – White marlin are found in deep tropical and warm temperate waters throughout the Atlantic Ocean including the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea, and the Western Mediterranean. They can be distinguished from other billfish by their rounded dorsal and anal fins. The maximum height of the largest lobe on the first dorsal fin is greater than the depth of the body. The coloration of the white marlin is a dorsal dark blue fading into a silver-white with brown spots. Spots also are present on the first dorsal fin of the fish.
White marlin have a tendency to be very acrobatic while on a line and present a very strong fight for one of the smaller species of billfish. “The maximum length for the white marlin is 110 in (280 cm) and maximum weight is approximately 180 lbs and usually ranges from 51-83 inches in body length.” (Florida Museum of Natural History). White marlin overtakes their baitfish prey with speed rather than using their bills to slash and stun.
Common Names of White Marlin (provided by ICCAT):
Azores Islands: Espadim branco
Barbados: White marlin
Benin: Ajètè, Adjètè
Brazil: Agulhão, Agulhão branco, Marlim branco
Canada: White marlin, Makaire blanc
Cape Verde: Espadim-branco do Atlântico
China: 白色四鳍旗鱼 (Bái sè sì chi chi-yu)
Côte d’Ivoire: Espadon
Cuba: Aguja blanca
Denmark: Hvid marlin
Dominican Republic: Aguja blanca
Finland: Valkomarliini
France: Makaire blanc
Germany: Weißer Marlin
Greece: Marlinos Atlantikou
Italy: Marlin bianco, Agguhia pilligrina
Japan: Nishimakajiki
Korea: Bag-sae-chi
Martinique: Varé, Makaire blanc Mexico: Marlin blanco
Morocco: Espadon
Namibia: Weißer Marlin
Netherlands Antilles: Balau Salmou, Balau kora
Norway: Hvit spydfisk
Portugal: Marlim-branco, Espadarte-branco
Puerto Rico: White marlin
Romania: Marlin alb
Russian Fed.: Belyi marlin
Senegal: Marlin blanc
South Africa: White marlin, Wit marlin
Spain: Aguja blanca, Marlin blanco
Trinidad y Tobago: White marlin
Uruguay: Marlin blanco
United Kingdom: Atlantic white marlin
United States of America: White marlin, Skilligalee
Venezuela: Aguja blanca, Palagar